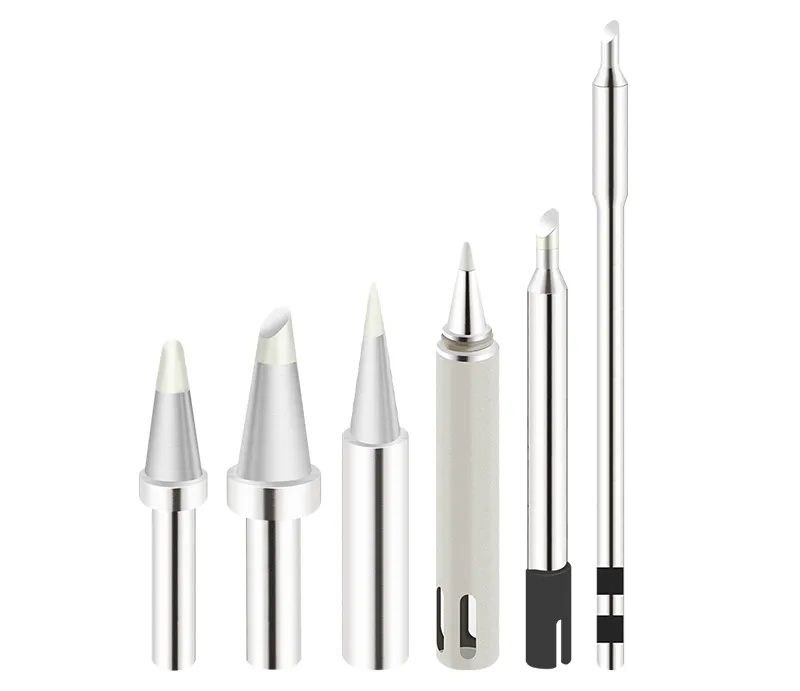
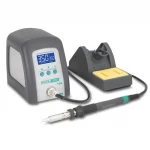
QUICK Solder Tip Series
- Fast heat transfer
- Oxidation resistant
- Long service life
- Suitable for automated production
- Stable soldering process
Contacts
Category: Intelligent soldering station
Solder Tip Selection
Choosing the correct size and shape of the soldering tip is very important. A suitable soldering tip improves efficiency and extends tip lifetime.
- The size of the soldering tip is directly related to its thermal capacity. When performing continuous soldering, using a larger tip helps reduce temperature drop.
- Additionally, because larger tips have greater thermal capacity, they allow soldering at lower temperatures, reducing oxidation and extending tip life.
- In general, tip size should be selected so that it does not affect surrounding components. Choosing a tip with the right shape and sufficient contact area improves soldering efficiency.
| Tip Type | Characteristics | Applications | Illustration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type I (Needle / Pointed) | Sharp, pointed tip | Suitable for fine details, narrow spaces, or removing solder bridges on small SMT components | 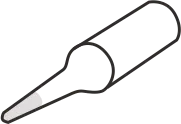  |
| Type B (Conical) | No directional limitation – the entire tip can be used for soldering | Suitable for general-purpose soldering and various pad sizes | 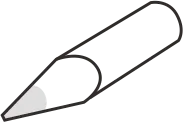 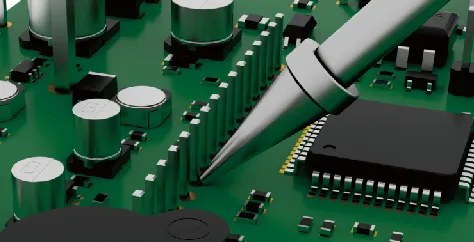 |
| Type D (Chisel) | Soldering using the flat end of the tip | Suitable for heavy soldering, large pads, thick leads, or areas requiring more solder |  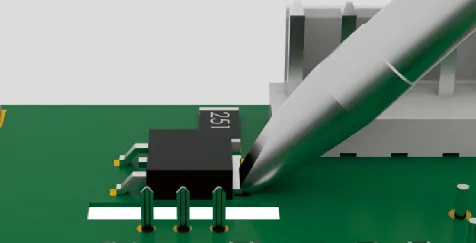 |
| Type C (Bevel) | Soldering using the beveled front surface | Similar to Type D – suitable for large areas, thick leads, and high-solder-volume joints | 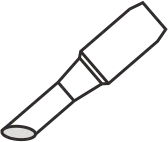 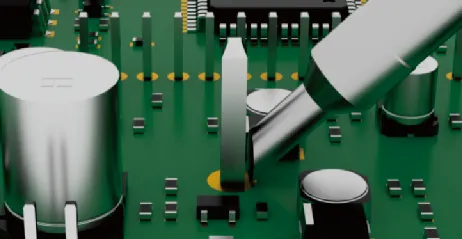 |
| Type K (Knife) | Soldering with the blade surface, suitable for drag and point soldering, highly versatile | Suitable for SOJ, PLCC, SOP, QFP, power components, ground planes, bridge removal, and connector soldering |   |
Usage and Maintenance
- When using a new soldering tip, set the temperature to 250–280℃ to apply a protective solder coating.
- Select the appropriate tip size according to the pad or component being soldered.
- To prevent tip oxidation, apply a layer of fresh solder before placing the tip back on the stand.
- The cleaning sponge should be damp but not soaking wet. This ensures effective cleaning while preventing rapid temperature drop. Using a dry sponge may damage the tip and reduce solder wetting.
- If oxidation occurs due to improper use, do not file or grind the coating. Instead, clean using a fine metal brush or restoration compound at low temperature (250–280℃).
- Do not press excessively while soldering, and avoid repeatedly soldering the same point unnecessarily.
- Prefer lower soldering temperatures, typically 320–380℃. If higher temperatures are continuously required, review whether the iron and tip combination is suitable.
Removing Solder Tip Oxidation
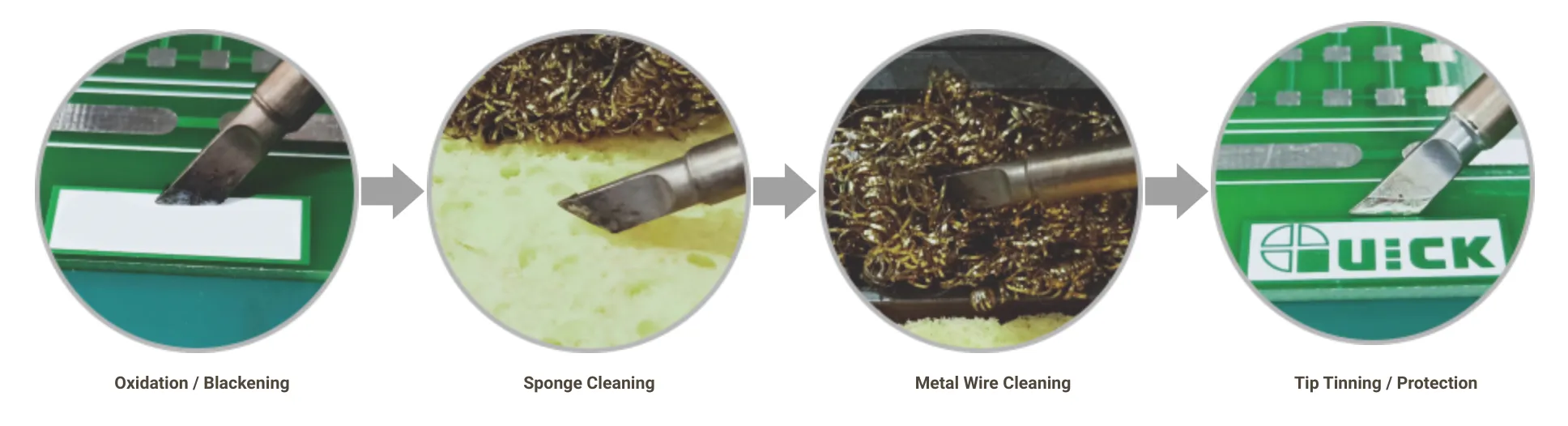

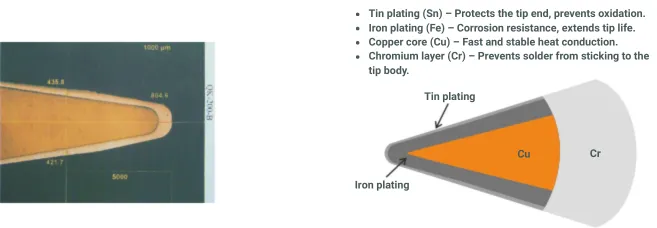
Solder Tip Cross-Section
Compatible Soldering Tips
Replacement Tips for QUICK TS1200 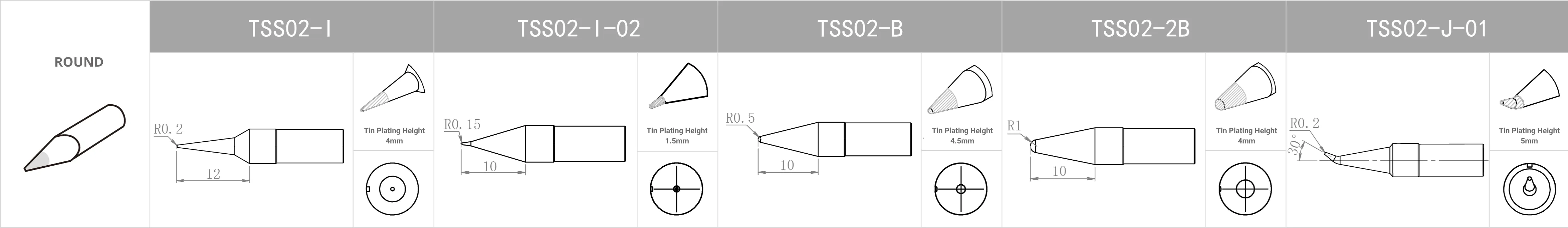
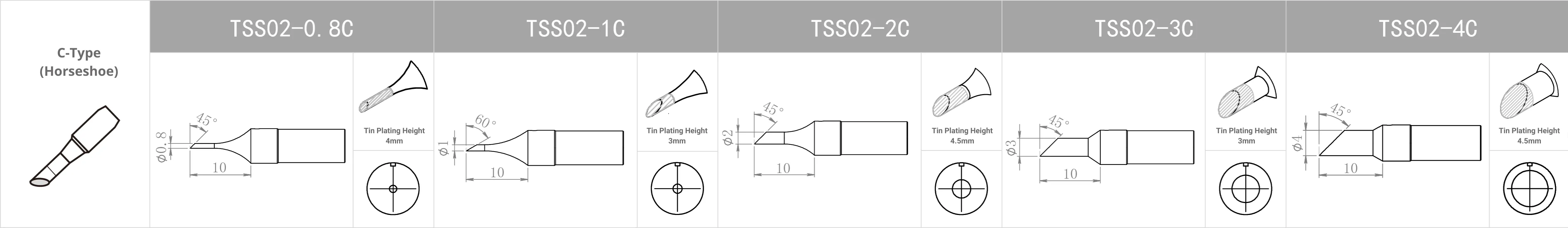
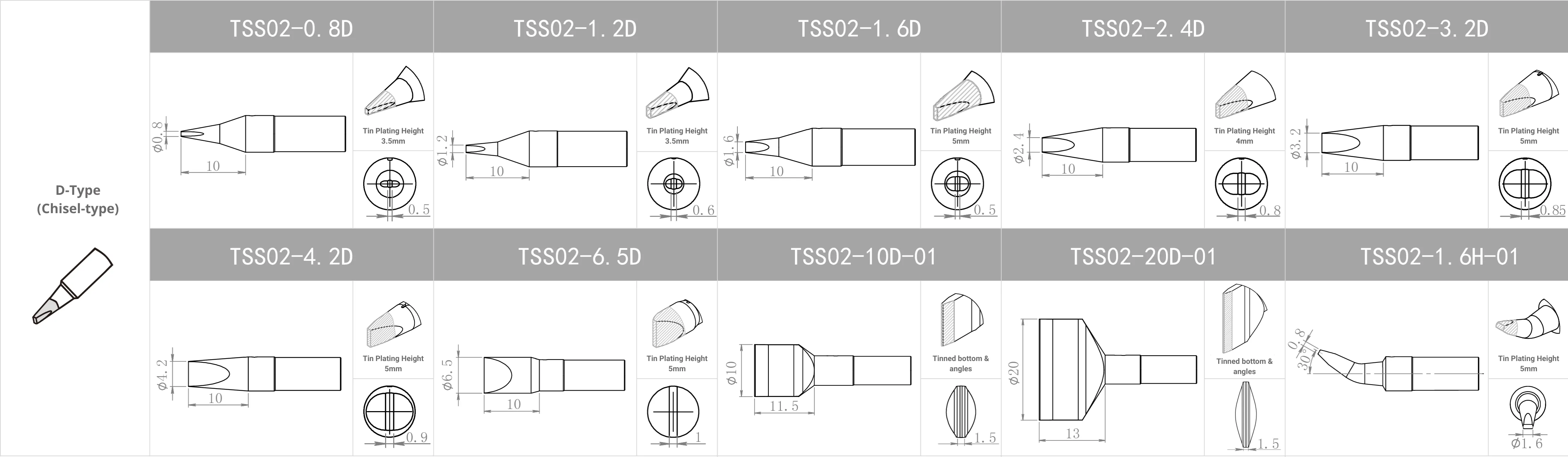
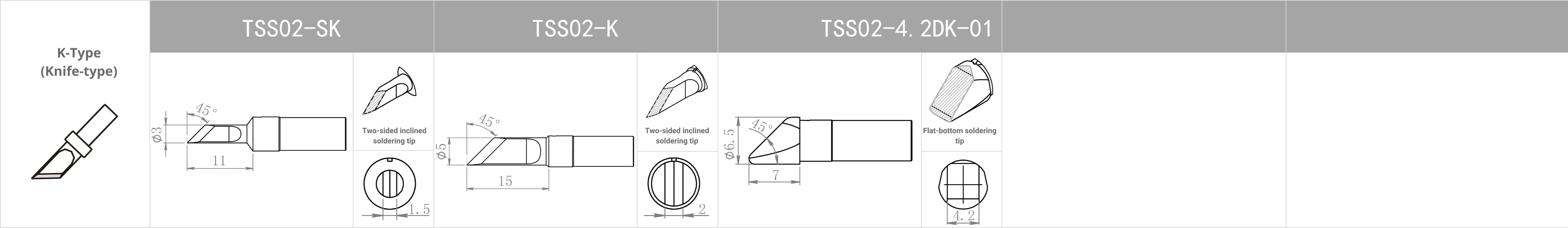 Replacement Tips for QUICK TS2200 / 203H / 503 / 504 / 203D / 376D
Replacement Tips for QUICK TS2200 / 203H / 503 / 504 / 203D / 376D 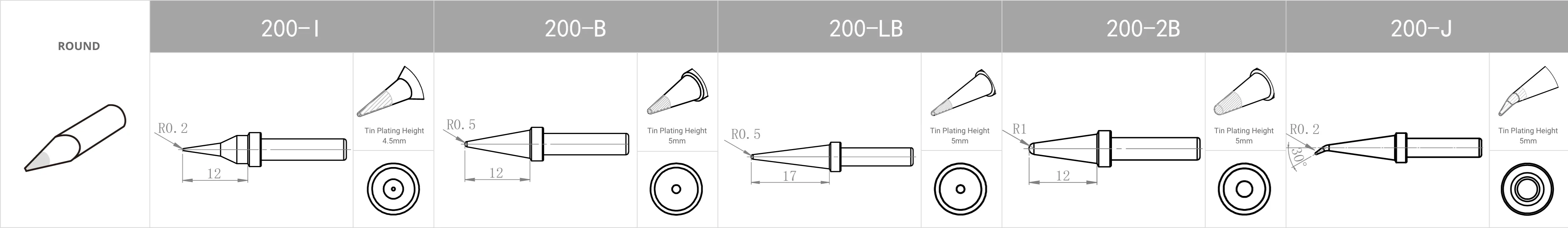
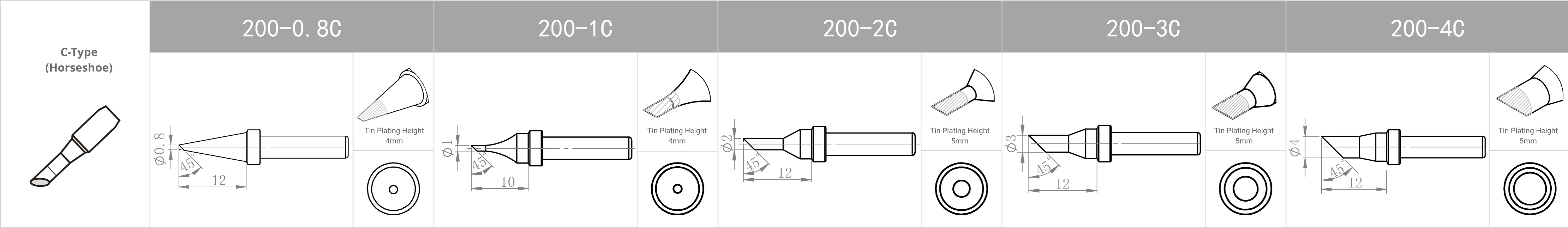
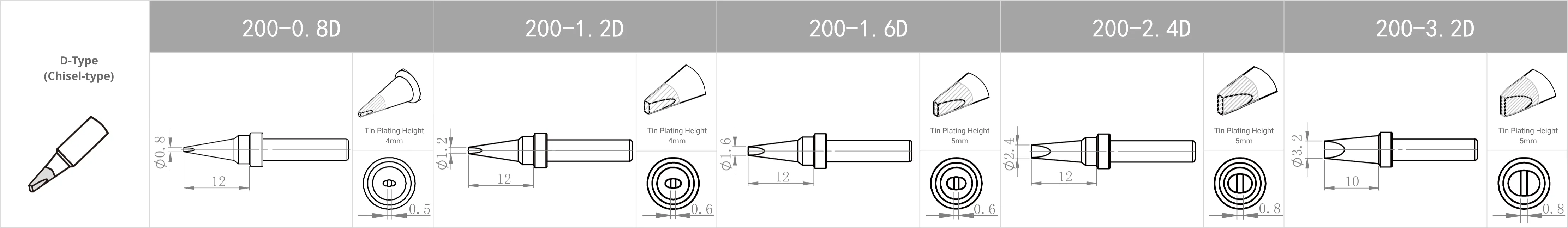
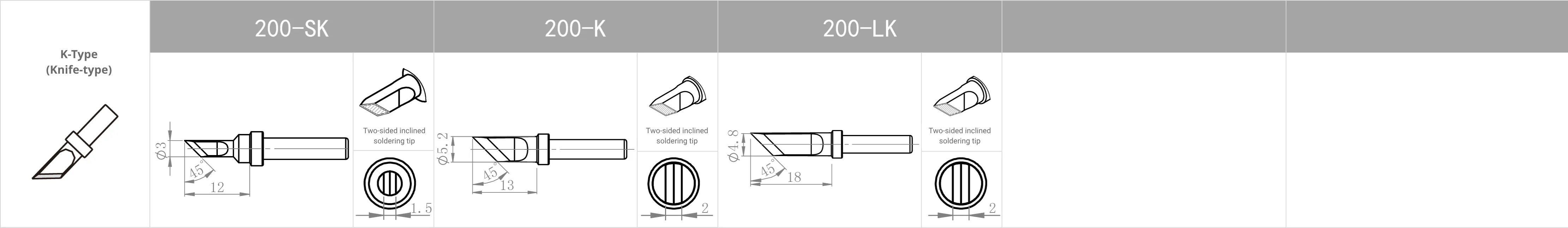 Replacement Tips for QUICK TS1100 / 236 / 969 / 967 / 375 (A+) / 375 (B+) / 3104
Replacement Tips for QUICK TS1100 / 236 / 969 / 967 / 375 (A+) / 375 (B+) / 3104 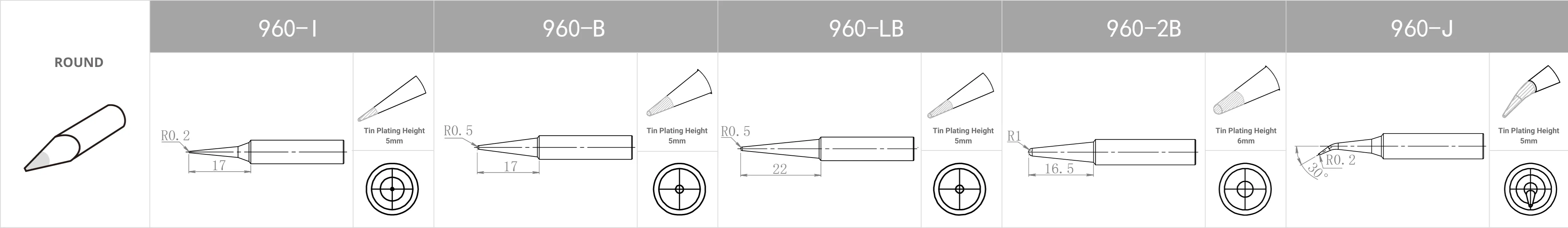
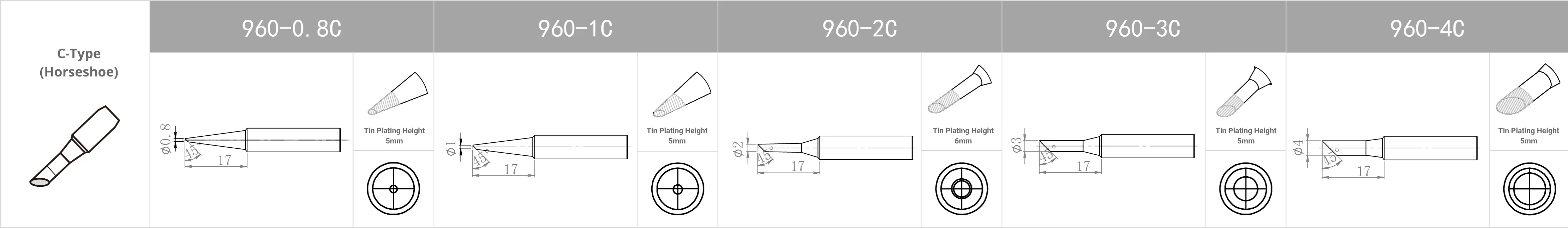
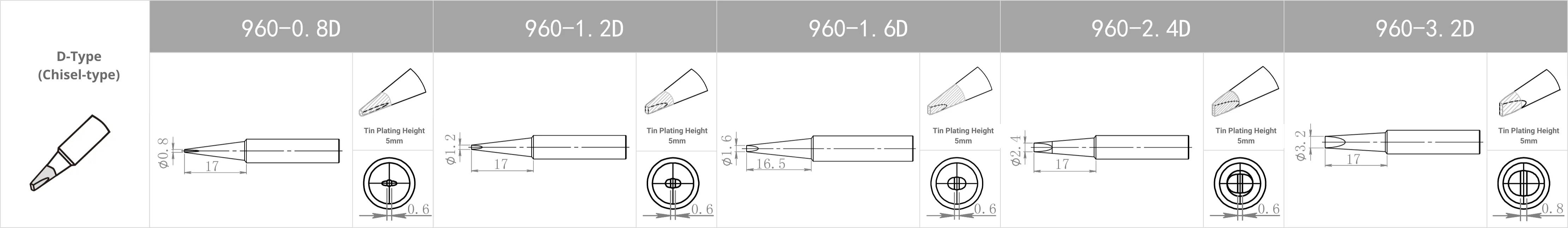
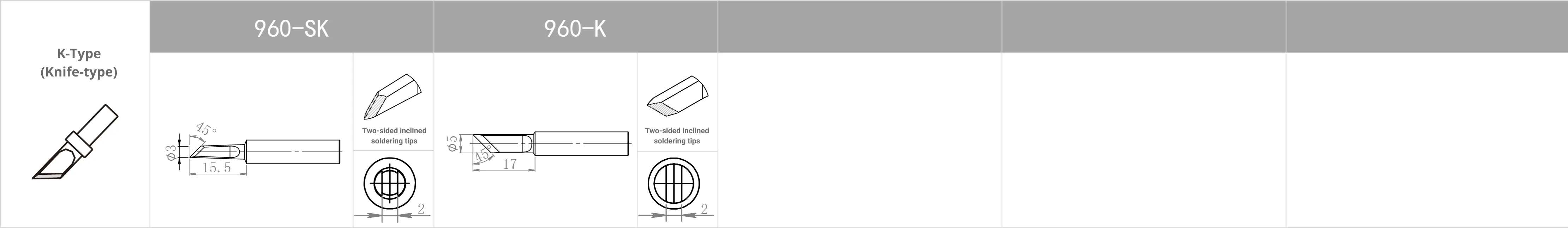 Replacement Tips for QUICK TS2300 / 205 / 3205 / 376D-150
Replacement Tips for QUICK TS2300 / 205 / 3205 / 376D-150 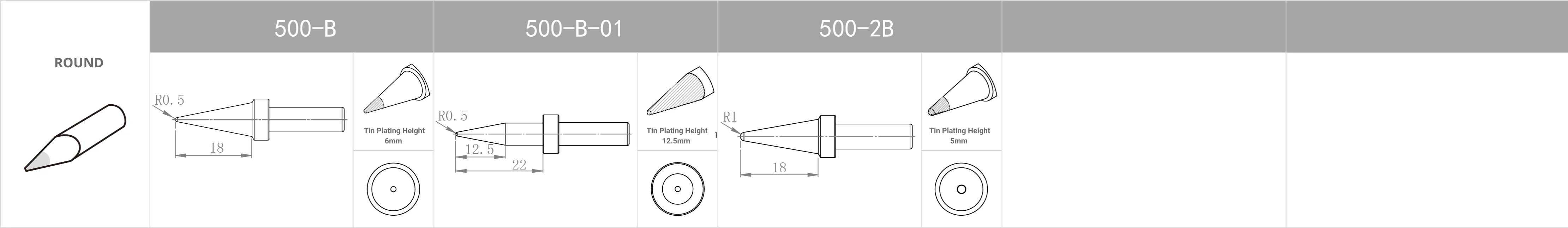
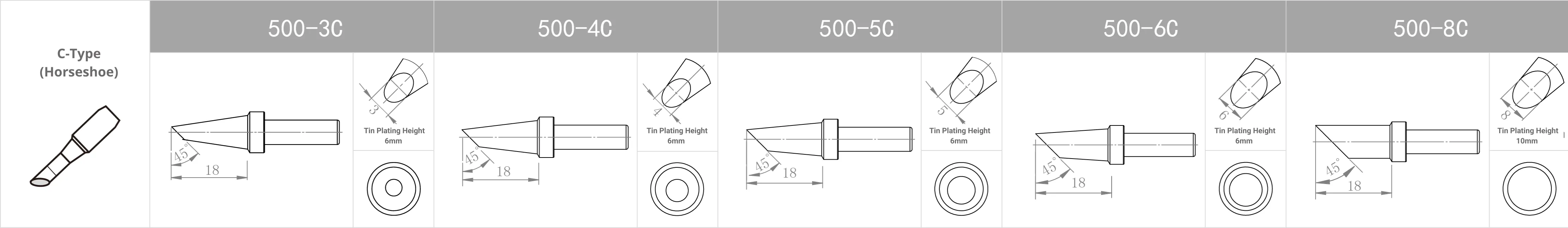
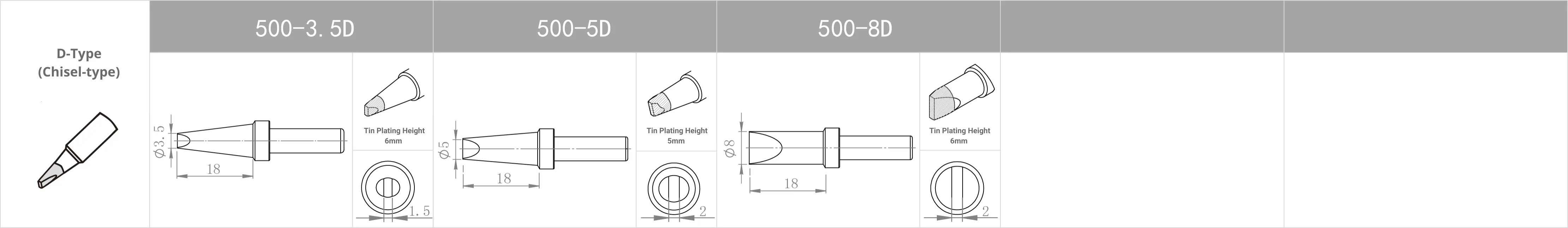
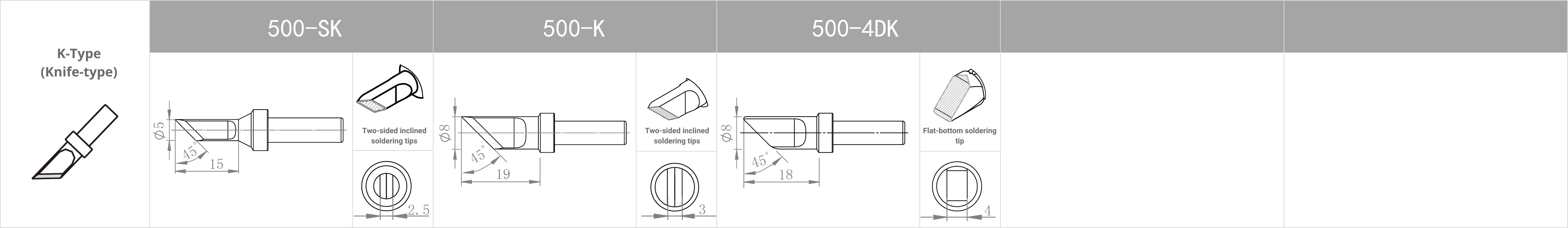 Replacement Tips for QUICK 303D
Replacement Tips for QUICK 303D 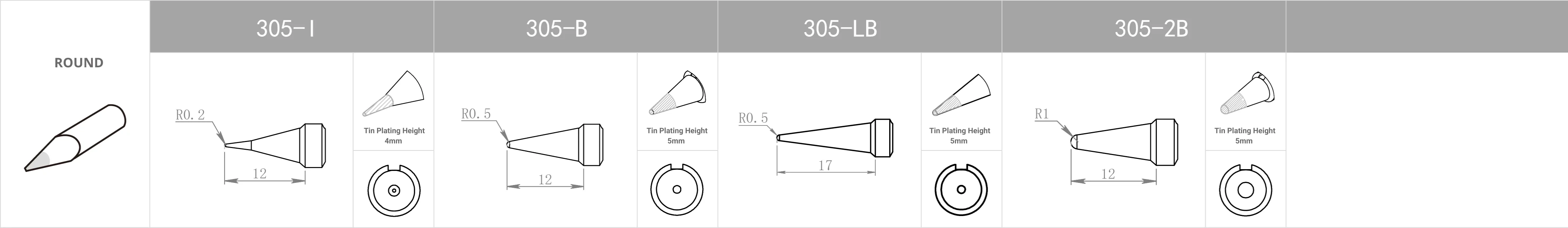
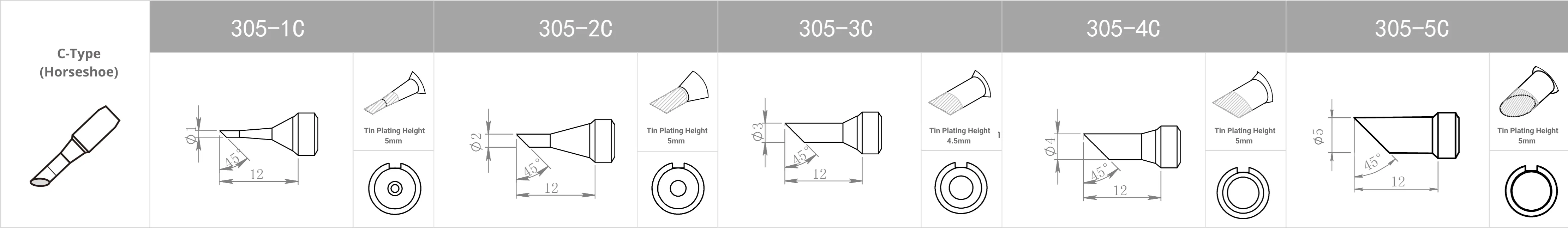
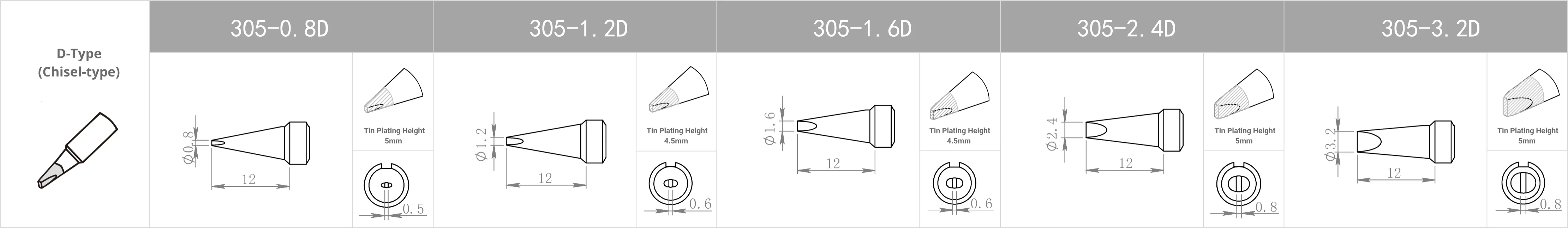
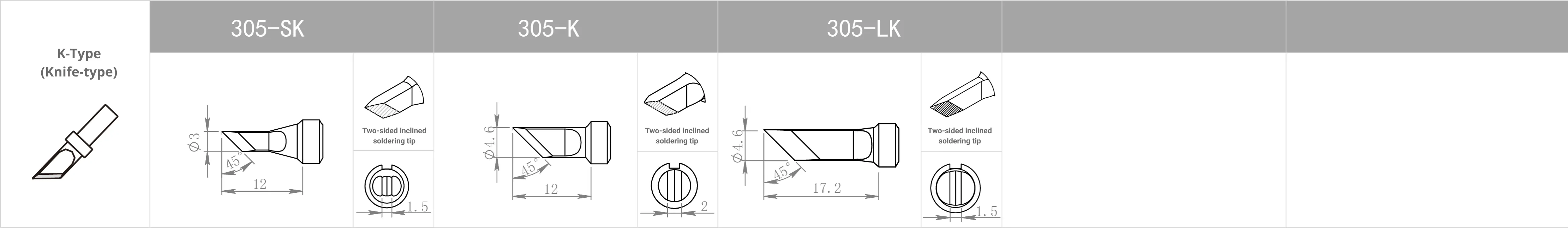 Replacement Tips for QUICK 3202 / 713
Replacement Tips for QUICK 3202 / 713 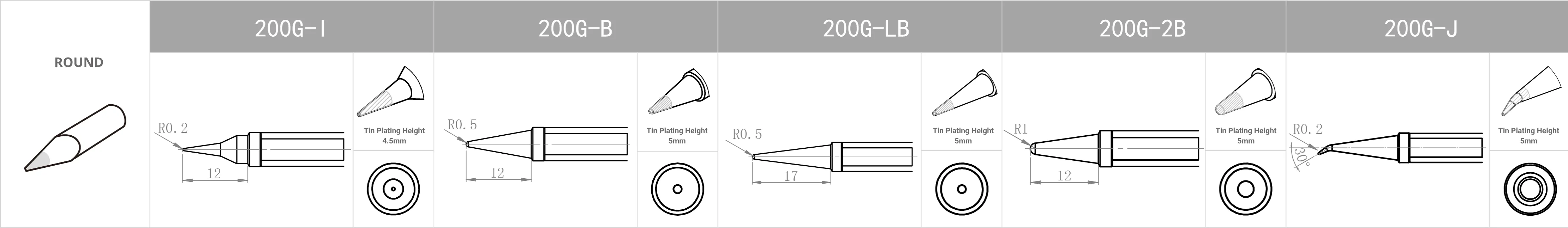
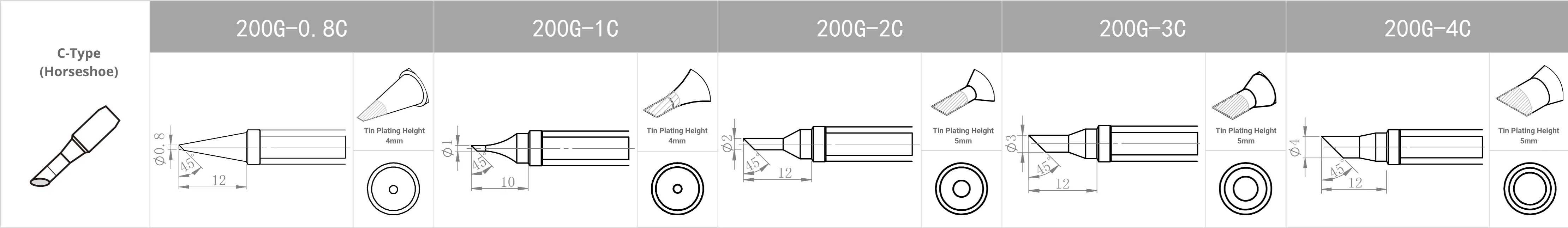
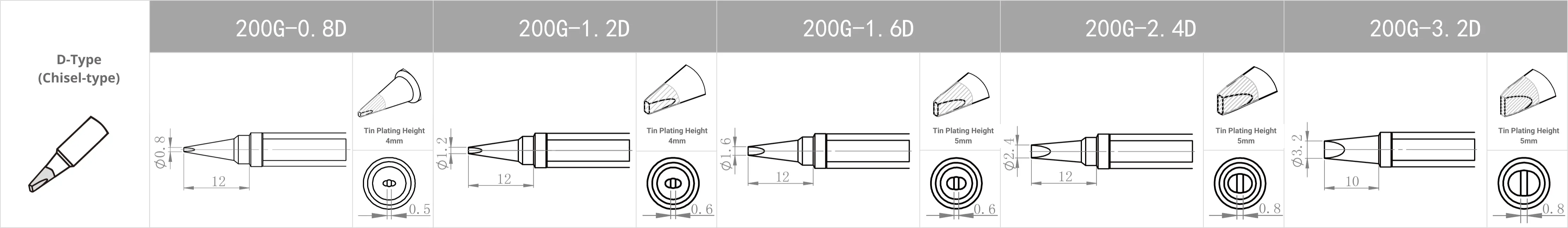
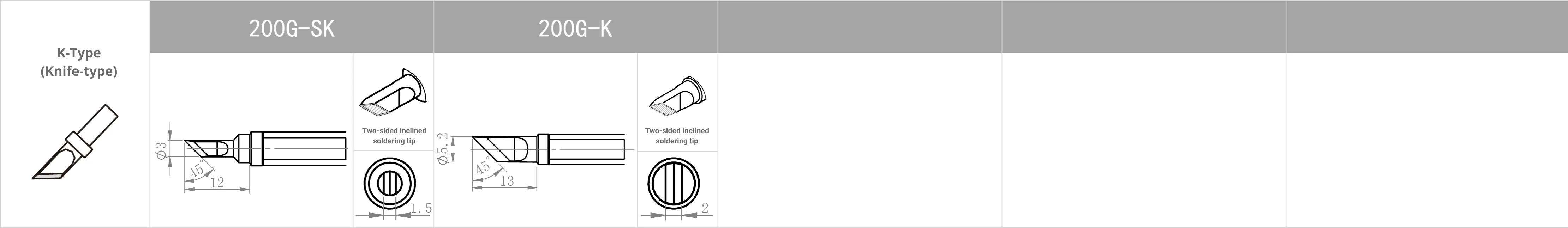



 Replacement Tips for QUICK TS2200 / 203H / 503 / 504 / 203D / 376D
Replacement Tips for QUICK TS2200 / 203H / 503 / 504 / 203D / 376D 


 Replacement Tips for QUICK TS1100 / 236 / 969 / 967 / 375 (A+) / 375 (B+) / 3104
Replacement Tips for QUICK TS1100 / 236 / 969 / 967 / 375 (A+) / 375 (B+) / 3104 


 Replacement Tips for QUICK TS2300 / 205 / 3205 / 376D-150
Replacement Tips for QUICK TS2300 / 205 / 3205 / 376D-150 


 Replacement Tips for QUICK 303D
Replacement Tips for QUICK 303D 


 Replacement Tips for QUICK 3202 / 713
Replacement Tips for QUICK 3202 / 713 



Related products